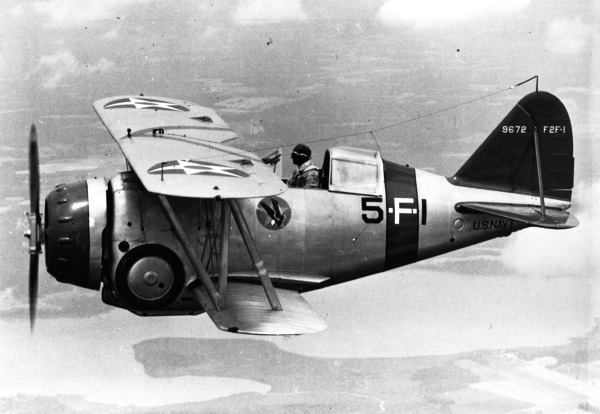

Design Development
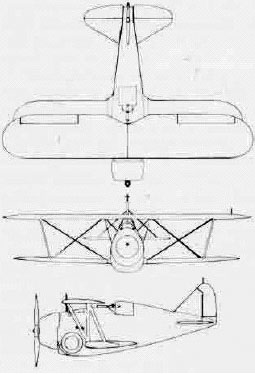 The outstanding performance of the Grumman FF-1 “Fifi” two-seat multirole aircraft, significantly faster than single-seat fighters of its day, prompted the Grumman design team to consider the potential of a single-seat version of the FF in 1932 already. In June Grumman submitted to the US Navy a carrier fighter proposal, the Grumman G-8. The navy accepted a prototype to be tested. The XF2F-1 prototype was completed in November the same year, slightly smaller than the FF, and with a semi-monocoque metal fuselage, reinforced metal wings, but the aileron and upper plane still canvas wrapped. It was a modern model with retractable landing gear, making the best of its engine.
The outstanding performance of the Grumman FF-1 “Fifi” two-seat multirole aircraft, significantly faster than single-seat fighters of its day, prompted the Grumman design team to consider the potential of a single-seat version of the FF in 1932 already. In June Grumman submitted to the US Navy a carrier fighter proposal, the Grumman G-8. The navy accepted a prototype to be tested. The XF2F-1 prototype was completed in November the same year, slightly smaller than the FF, and with a semi-monocoque metal fuselage, reinforced metal wings, but the aileron and upper plane still canvas wrapped. It was a modern model with retractable landing gear, making the best of its engine.
With its initial Power plant, the Pratt & Whitney XR-1534-44 Twin Wasp Junior (which developed 625 HP) but was still experimental, the prototype was also fitted with two standard 0.8-in (7.62 mm) M1919A4 Browning machine guns in the upper forward fuselage. The wings had mounts socket provision to mount two 50 kg bombs. But Grumman also brought to the design sealed watertight compartments in order to improve the chances of survival of the crew in case of splashdown due to the extra buoyancy.
The prototype made its maiden flight on October 18, 1933 in a configuration very close already to what the Navy might want. Jimmy Collins, Grumman’s test pilot was at the controls, and reached 369 km/h () at 2,560 meters () of altitude at this occasion, which was 35 km/h faster than the FF-1 at the same altitude. He also proved maneuverability was superior (as expected) to the FF-1 as well, so far better suited as a fighter (Which was one of the FF roles already).
After Grumman’s own evaluations, the XF2F-1 (Note there was no F1F in Grumman’s lineage, the place was taken by the FF-1, a different code for a different role) was placed in the hands of the Navy for official tests, over a six-month program of evaluation.
Navy test pilot pushed it to a maximum speed of 370 km/h at 2,500 m alt. () and established a climbing speed of 940 m per minute (ft second) but it should be noted that the stubby, stocky fuselage suffered from directional instability, pilots also noted its tendency to spin in an unsafe way. Thus the Navy praised the performances but asked Grumman minor to improved the noted issues. Grumman added a larger canopy for better visibility, made a 15 cm () increase in wingspan for the upper plane only, replaced the NACA hood with one of a smaller diameter, with distinctive droplet shaped fairings for the cylinder heads.
The modified XF2F-1 flew again in May 1934, and was eccapted by the Navy for service on its carriers. Thus, were ordered 54 production F2F-1 fighters on May 17, 1934.
PRODUCTION
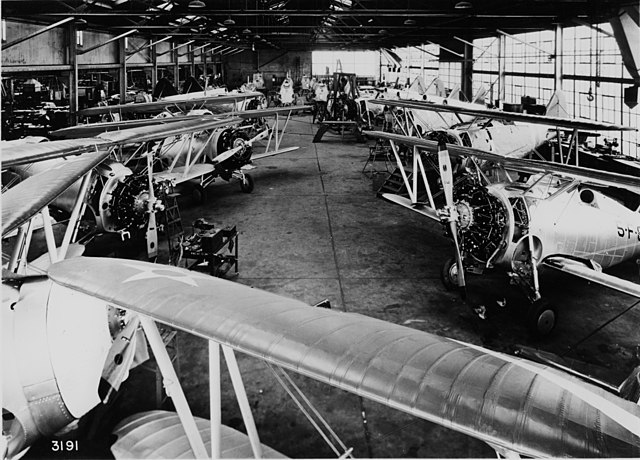

The first production F2F-1 was delivered on January 28, 1935, the last 10 months later. This was a short production run, because Grumman in between already had worked on its successor, the F3F. An additional prototype was ordered to replace the one that crashed on March 16, 1935, for a total number of 55 F2F-1s delivered in all. But this was only serie. Instead of an improved F2F-2 as asked by the Navy, Grumman went with another proposal, radically improved, which became the very last USN biplane fighter in 1936, the F3F, and direct predecessor of the monoplane F4F Wildcat.
VARIANTS & EVOLUTION
XF2F-1: USN designation for the Grumman Model G-8 prototype (625 hp -466 kW- XR-1534-44 Twin Wasp Junior radial engine), only one delivered.
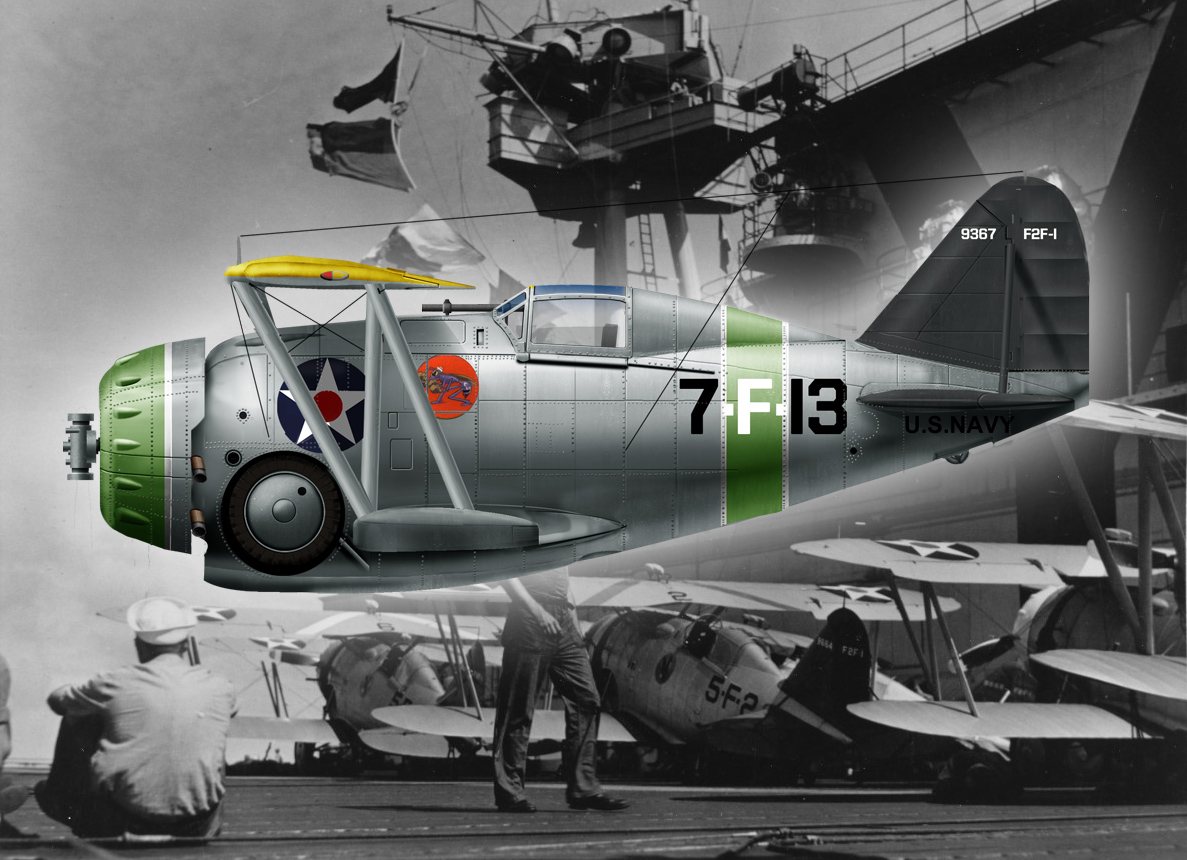
F2F-1: Sole production variant, 700 hp (522 kW) R-1535-72 Twin Wasp Junior radial engine: 55 built.
The F2F-1 differed from the prototype by its upper wing 6in longer in span, enlarged cockpit canopy, smoother, smaller NACA cowling with streamlined blisters over the cylinders. The Pratt & Whitney R-1535-72 Twin Wasp Junior was rated at 650hp and up to 700hp depending on the regime. Top speed of 231mph stayd very close to the prototype.
No F2F-2, but the Navy wanted on 15 October 1934 an improved prototype called XF3F-1.
The F3F was clearly related to the F2F, and order was placed even before F2F deliveries started. The Navy added a reinforced cell to perform ground attack while maintaining fighter performances and better maintenance and supply access, cheaper overall, but it was to be powered by the very same Pratt & Whitney R-1535-72 Twin Wasp Junior engine.
Engineers found solutions with a lenghtened and strenghtened fuselage, increased wing area, reduced wheel diameter to increase fuselage streamlining, but all the rest was stright from the Grumman F2F.
The first F3F, BuNo. 9727 was delivered on 20 March 1935 to factory’s test pilot Jimmy Collins, noted corrections to make, two days later during testing bombing capabilities at the 10th dive when recovering, sensors registed 14 g and wings broke in mid-air. This resulted in a rapid crash, causing the death of Jimmy Collins, a hard blow for Leroy Grumman and all his staff, needless to say for the family. All because the Navy wanted a fighter that can double as dive bomber… to later relinquish this specification.
The F2F service
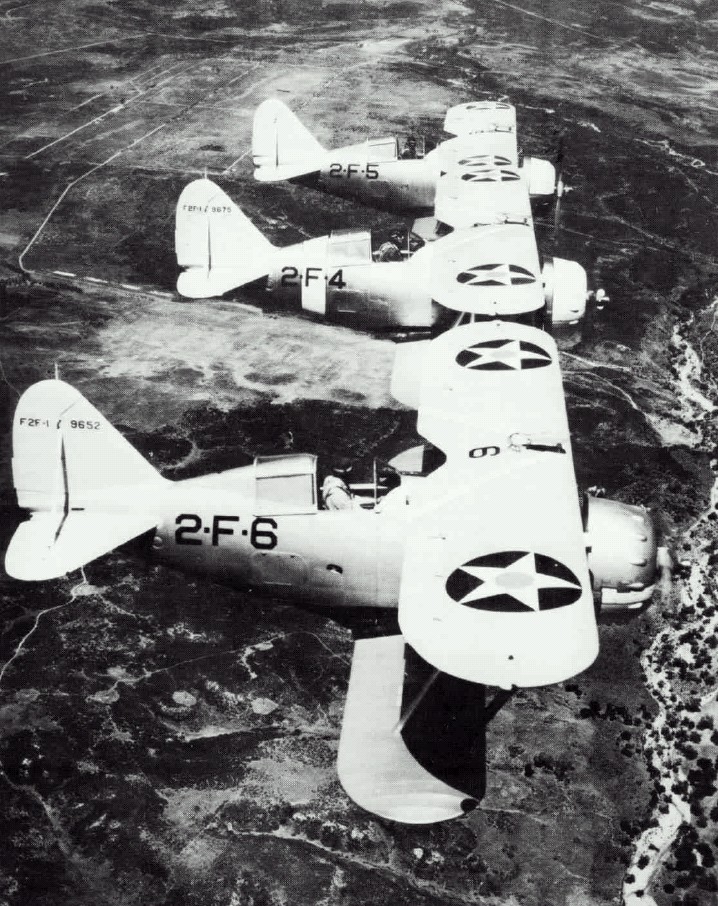

The serial F2F were first delivered on 19 January 1935. They served with front-line squadrons from 1935 to late 1939. F2F-1s began to replace the Boeing F4B-2s of VF-2B, stationed on the aircraft carrier USS Lexington, on February 19, 1935.
The first squadron converting was indeed VF-2B (‘Fighting Two’, USS Lexington) as they arrived to start later pilot qualifications from 19 February 1935, and she had fully converted her fighter squadron by the middle of the year. These were ultimately retired on 30 September 1940, the surviving 18 aircraft sent to NAS Pensacola to end as advanced trainers.
The second squadron was VF-3B (USS Ranger) also converted by mid-1935. The squadron moved ship twice, swapping to USS Yorktown in 1937 as VF-7B and then VF-5 to reflect Yorktown’s new pennant CV-5. The squadron converted to the Grumman F3F in 1939.
The F2F-1 briefly was used used in VF-5B as an interim before receiving the F3F-1 in 1936. VF-7 used 2 F2F-1s and VF-4M (later VMF-2) 3 F2F-1s also in 1937, again before F3F-1 arrived.
The F2Fs became a perfect advance trainer in its second carrer from 1937-38, as gunnery platform notably, and pilot appreciated to swap from the very similar F2F and F3F. The F2F was attached to various Naval Air Stations and patrol wings but ended in 1940-41 with NAS Miami and NAS Pensacola, the last F2F-1 retired in 1942, although some sources stated it was used until 1943.
The F2F-1 had a relatively good service career for its time, serving in limited front-line squadrons from 1935 to 1939 on carriers, and to September 1940 in land units only as F3F-3s were received as replacements. It completely replaced in all fighter squadrons, but continued to be used as a fire trainer and utility aircraft at various naval air bases until declared “surplus to requirement” in 1942 the remaining planes were scrapped. The technological gap was just to great between the F2F and Wilcat, let alone the Hellcat that was just entering service.
It seems unfortunately none survived to this day, they were all scrapped untlike the F3F.
⚙ PLANE specifications |
|
| Empty Weight | 2,691 lb (1,221 kg) |
| Max Takeoff weight | 3,847 lb (1,745 kg) |
| Lenght | 21 ft 5 in (6.53 m) |
| Wingspan | 28 ft 6 in (8.69 m) |
| Height | 9 ft 1 in (2.77 m) |
| Wing Area | 230 sq ft (21.4 m2) |
| Engine | Pratt & Whitney R-1535-72 Twin Wasp Junior radial engine, 700 hp (522 kW) |
| Top Speed, sea level | 231 mph (372 km/h, 201 kn) |
| Range | 985 mi (1,585 km, 857 nmi) |
| Climb Rate | 2,050 ft/min (10.4 m/s) |
| Ceiling | 27,100 ft (8,260 m) |
| Armament | 2× .30-in machine guns |
| Crew | 1 Pilot |
Read More
Books
Cacutt, Len, ed. “Grumman Single-Seat Biplane Fighters.” Great Aircraft of the World. London: Marshall Cavendish, 1989.
Dann, Richard LCDR, ed. “Grumman Biplane Fighters in Action.” Carrollton, TX: Squadron Signal, 1993.
Graff, Cory. F6F Hellcat at War. New York: Zenith Imprint, 2009.
Swanborough, Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. United States Navy Aircraft since 1911. London: Putnam, Second edition, 1976.
Naval Fighters – Grumman F2F and F3F (pre-war Navy/Marine biplane fighters & Civilian Variants By Richard S. Dann
Links
cradleofaviation.org grummans_ascendancy
on militaryfactory.com/
commons.wikimedia.org/ cc photos
on en.wikipedia.org
on airvectors.net
on historyofwar.org/
on aviastar.org
on armedconflicts.com/
Model Kits
General Query on Scalemates
Plenty of choice, but far less than the F3F or F4F understandably. Especially old kits, starting at 1:17, then 1:24, 1:48, and plethora of 1:72. Trumpeter made squadrons of them at 1:350 and 1:700 to pupolate CVs. Among the recent ones, F2F-1 from Attack Squadron (kit # 72068), 1:72 scale. Review of the latter.
3D
Kampflieger 1/144 3d print model
Video
Rex Hangar’s F2F and F3F.

F2F-1 from VF-5, 1937, USS Yorktown.

F2F-1 VF-7, 1940 Neutrality Patrol, aboard CV-7 USS Wasp.

F3F-1 aboard USS Lexington, 1937, to compare.
Photos
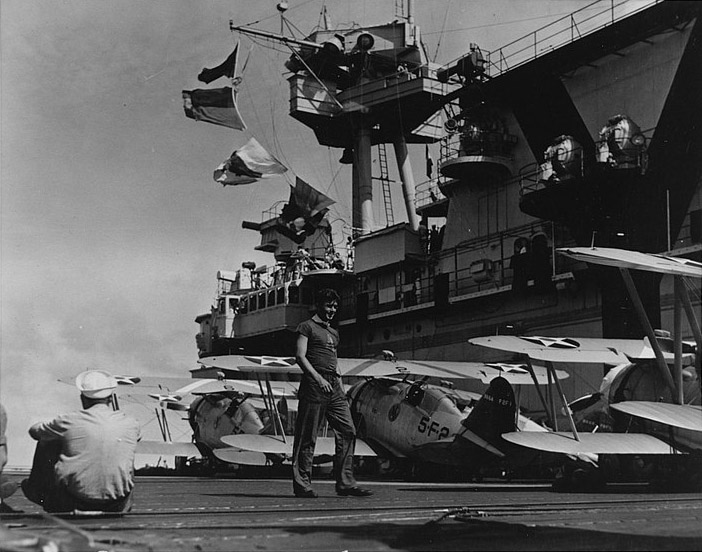

Onboard USS Yorktown 1939
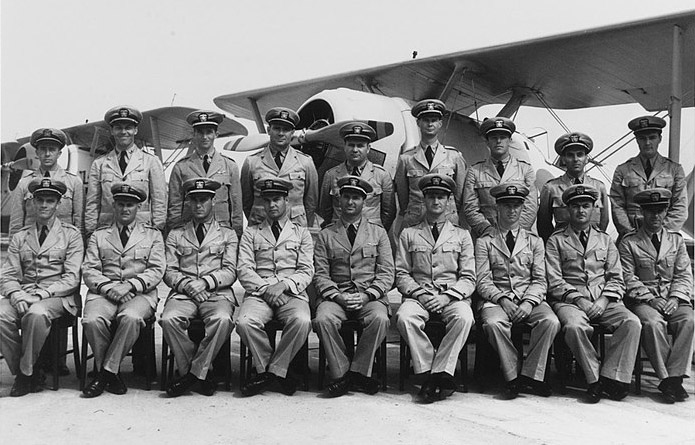

F2F-1 of FV-5

Ray Wagner Coll. F2F-1

Ray Wagner Coll. F2F-1
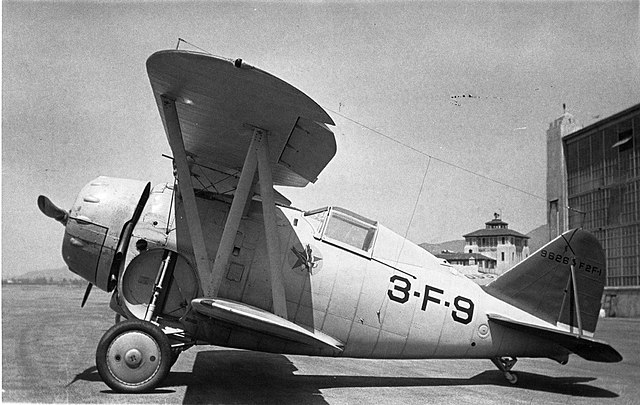

F2F-1 from VF-3B, Burbank circa 1936, Ludlow

F1F-1
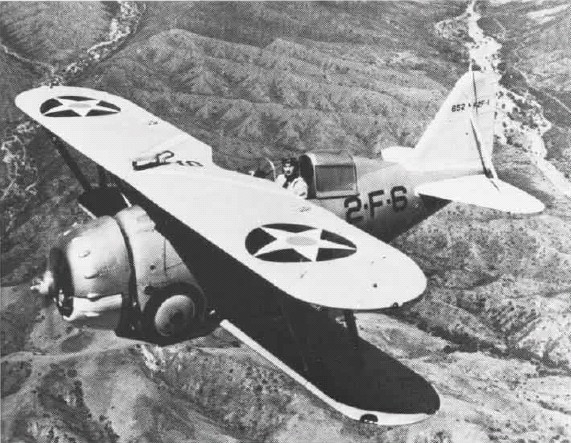

F2F-1, 2F6 NAN
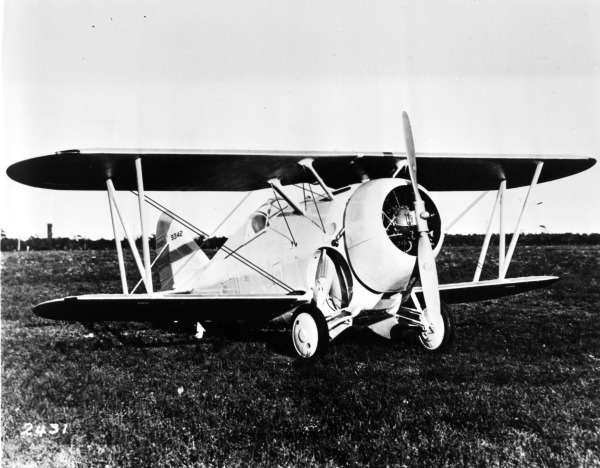

F2F-1, Ray Wagner Coll.







 Latest Facebook Entry -
Latest Facebook Entry -  X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive
X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive Instagram (@navalencyc)
Instagram (@navalencyc)





 French Navy
French Navy Royal Navy
Royal Navy Russian Navy
Russian Navy Armada Espanola
Armada Espanola Austrian Navy
Austrian Navy K.u.K. Kriegsmarine
K.u.K. Kriegsmarine Dansk Marine
Dansk Marine Nautiko Hellenon
Nautiko Hellenon Koninklije Marine 1870
Koninklije Marine 1870 Marinha do Brasil
Marinha do Brasil Osmanlı Donanması
Osmanlı Donanması Marina Do Peru
Marina Do Peru Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Regia Marina 1870
Regia Marina 1870 Nihhon Kaigun 1870
Nihhon Kaigun 1870 Preußische Marine 1870
Preußische Marine 1870 Russkiy Flot 1870
Russkiy Flot 1870 Svenska marinen
Svenska marinen Søværnet
Søværnet Union Navy
Union Navy Confederate Navy
Confederate Navy Armada de Argentina
Armada de Argentina Imperial Chinese Navy
Imperial Chinese Navy Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Mexico
Mexico Kaiserliche Marine
Kaiserliche Marine 1898 US Navy
1898 US Navy Sovietskiy Flot
Sovietskiy Flot Royal Canadian Navy
Royal Canadian Navy Royal Australian Navy
Royal Australian Navy RNZN Fleet
RNZN Fleet Chinese Navy 1937
Chinese Navy 1937 Kriegsmarine
Kriegsmarine Chilean Navy
Chilean Navy Danish Navy
Danish Navy Finnish Navy
Finnish Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Polish Navy
Polish Navy Romanian Navy
Romanian Navy Turkish Navy
Turkish Navy Royal Yugoslav Navy
Royal Yugoslav Navy Royal Thai Navy
Royal Thai Navy Minor Navies
Minor Navies Albania
Albania Austria
Austria Belgium
Belgium Columbia
Columbia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cuba
Cuba Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Haiti
Haiti Hungary
Hungary Honduras
Honduras Estonia
Estonia Iceland
Iceland Eire
Eire Equador
Equador Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Latvia
Latvia Liberia
Liberia Lithuania
Lithuania Mandchukuo
Mandchukuo Morocco
Morocco Nicaragua
Nicaragua Persia
Persia San Salvador
San Salvador Sarawak
Sarawak Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela Zanzibar
Zanzibar Warsaw Pact Navies
Warsaw Pact Navies Bulgaria
Bulgaria Hungary
Hungary

 Bundesmarine
Bundesmarine Dutch Navy
Dutch Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Marina Militare
Marina Militare Yugoslav Navy
Yugoslav Navy Chinese Navy
Chinese Navy Indian Navy
Indian Navy Indonesian Navy
Indonesian Navy JMSDF
JMSDF North Korean Navy
North Korean Navy Pakistani Navy
Pakistani Navy Philippines Navy
Philippines Navy ROKN
ROKN Rep. of Singapore Navy
Rep. of Singapore Navy Taiwanese Navy
Taiwanese Navy IDF Navy
IDF Navy Saudi Navy
Saudi Navy Royal New Zealand Navy
Royal New Zealand Navy Egyptian Navy
Egyptian Navy South African Navy
South African Navy






























 Ukrainian Navy
Ukrainian Navy dbodesign
dbodesign