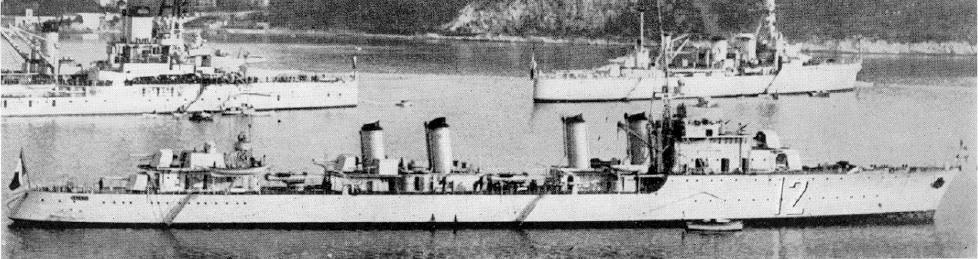
 French Navy – Contre-Torpilleurs de 2400 tonnes. 6 built 1927-1930, in service until 1942: Guepard, Valmy, Verdun, Bison, Lion, Vauban.
French Navy – Contre-Torpilleurs de 2400 tonnes. 6 built 1927-1930, in service until 1942: Guepard, Valmy, Verdun, Bison, Lion, Vauban.The Guepard class destroyers were a follow-up of the Jaguar class built in 1922-25. They were retrospectively called the “2400 tonnes” by contrast to the previous “2100” tonnes and officially were called “contre-torpilleurs”, since the standard or “1500 tonnes” destroyers built in the same decade were called “torpilleurs”. They were not torpedo boats in any way but destroyers. The Guepard were large destroyers, quite unique for their time. Inspirations came from war prize such as the ex-S113 and British RN flotilla leaders of 1917-1918. Their role was very different from the “torpilleurs” as they were essentially scouts for the battle fleet.

The Marine Nationale thus built a serie of uniform classes of such “contre-torpilleurs”, successively 2100, and three classes of 2400 tonnes ships, the Guepard, Aigle and Vauquelin class. They were quite uniform in design and a true departure from the previous Jaguar class. Not only they were larger, but also possessed a better range and four funnels versus three on the Jaguar (also called Chacal in many publications). The Guepard class were those which introduced this new standard, based on the experience gained with the six Jaguar class.
These vessels were called also “conducteurs de flottille” (literal translation or flotilla leaders) as their secondary role was indeed to lead 1500t standard destroyers formations, but also hunt down enemy destroyers and face enemy light scouts. For their missions they required high speed in all weather, good endurance and a powerful armament to attack and defend themselves. The French, in order to give them a qualitative edge, looked at beefing up their capabilities, and instead of the usual 120-127 mm gave them 5.5 inches or 130 mm main guns, and instead of 533 mm or 21 inches torpedo tubes, 550 mm was the French standard. On paper, this gave them a better impact. However at large, with a standard displacement of 2440 tonnes and fully loaded of 3400 tonnes, they looked still a bit under-armed and lacking speed. 36 knots was average, not stellar, but this was their fully loaded speed. On trials they reached 40 knots. This was even beaten in 1932 with the Fantasque class, capable of 37 knots FL as designed, but up to 42.5 knots on trials, with new improved main guns and more torpedo tubes.
The Guépard-class were six ships laid down in 1927 and commissioned in 1930, roughly similar to the previous Jaguar class, but with a larger hull and slightly improved plus a new gun armament with 138 mm guns (5.5 in)/40 of a new design. They were to be all named after animals of prey like the previous class, but by political decision, three were given “V” names, two battles and a field-marshal. The Guepard class fought in World War II but apart Bison sunk by the Luftwaffe in Norway in May 1940, all remaining ones were scuttled in Toulon on 27 November 1942.
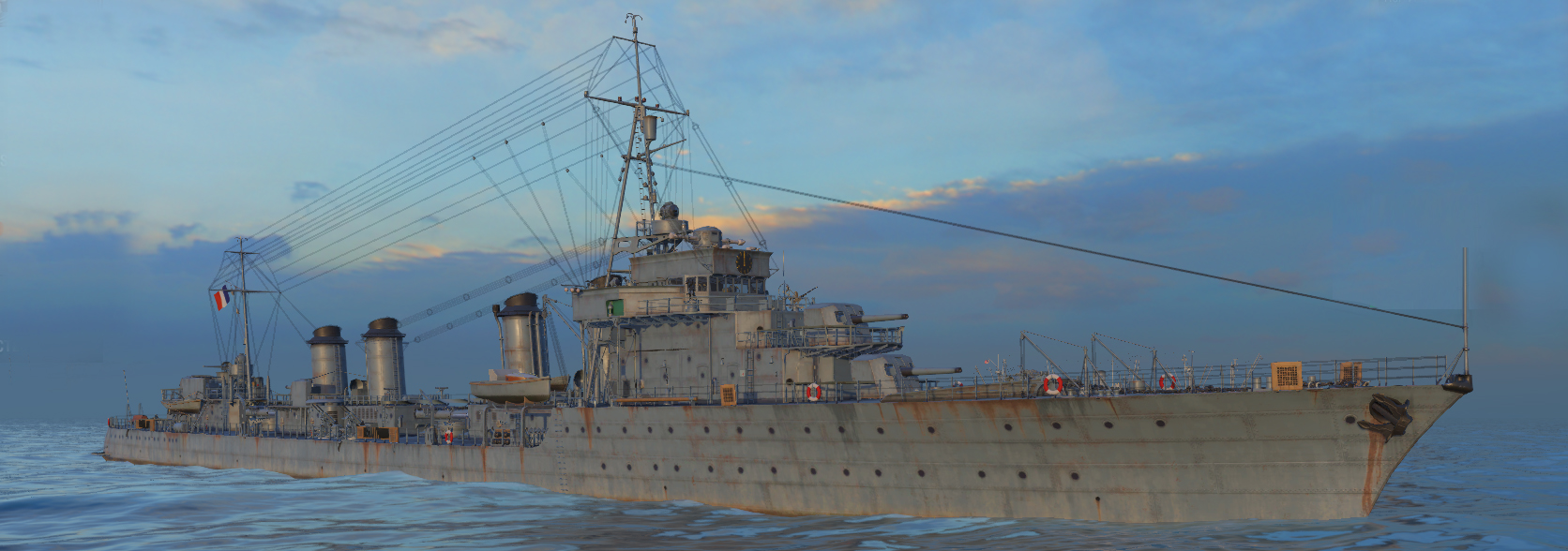


⚙ Guepard class specs. |
|
| Displacement | 2,436 t (2,398 long tons) standard, 3,220 t (3,170 long tons) full load |
| Dimensions | 130.2 x 11.5 x 4.3m (427 ft 2 in x 37 ft 9 in x 14 ft 1 in) |
| Propulsion | 2 shafts, geared steam turbines, 4 du Temple boilers 64,000 PS (47,000 kW; 63,000 shp) |
| Speed | 35.5 knots (65.7 km/h; 40.9 mph) (40 kts on trials) |
| Range | 3,000 nmi (5,600 km; 3,500 mi) at 15 knots (28 km/h; 17 mph) |
| Armament | 5× 138.6 mm/40, 4× 37 mm AA, 4× 13.2 mm AA, 2×3 550 mm TTs, 28 DCs |
| Sensors | Hydrophones, Radars (1942) |
| Crew | 12 officers, 224 crewmen (wartime) |
Career of the Guepard class
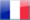
Destroyer Guepard -ONI203 booklet for identification of ships of the French Navy -PD (cc)
 Guepard
Guepard
Guépard (“Cheetah”) was Built by Arsenal de Lorient, laid down on xxx, launched on, Completed 13 August 1929, Scuttled 27 November 1942. Refloated 4 September 1943. Bombed and sunk March 1944 Refloated 1947 and broken up.
 Valmy
Valmy
Valmy (named after the battle of Valmy) was Built by Ateliers et Chantiers de St Nazaire-Penhoët, St. Nazaire, Completed 1 January 1930.
She was scuttled, Seized by Germans 27 November 1942, Refloated 15 March 1943 and began refit as Italian Navy FR 24, Captured by Germans at Savona September 1943. Wreck found at Genoa 1945 and broken up.
 Verdun
Verdun
Verdun was named after the battle of 1916. She was Built by Ateliers et Chantiers de la Loire, St Nazaire, Completed 1 April 1930. Scuttled 27 November 1942. Refloated 29 September 1943. Bombed and sunk 1944, Refloated 1948 and broken up in Italy.
 Bison
Bison
Bison was built by Arsenal de Lorient, Completed 10 October 1930. She was sunk by German Junkers Ju 87 Stukas while taking part in the evacuation of Namsos, on 3 May 1940, off Trondheim. Out of 229 members on the crew, 136 were lost. Survivors from Bison were picked up by HMS Afridi, which was then also sunk by the Stukas.
 Lion
Lion
Lion was Built by Ateliers et Chantiers de France, Dunkirk. Completed 21 January 1931. Scuttles Nov. and seized by Germans 27 November 1942. Given to Italy and entered service as FR 21. Scuttled at La Spezia 9 September 1943.
 Vauban
Vauban
Vauban (named after Marshal Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban) was built by Ateliers et Chantiers de France, Dunkirk, Completed 9 January 1931. Scuttled 27 November 1942. Never refloated by the axis. Refloated 12 May 1947 and broken up.
Read More/Src
Books
Cernuschi, Enrico & O’Hara, Vincent P. (2013). “Toulon: The Self-Destruction and Salvage of the French Fleet”. In Jordan, John (ed.). Warship 2013.
Chesneau, Roger, ed. (1980). Conway’s All the World’s Fighting Ships 1922–1946. Greenwich, UK: Conway Maritime Press.
Jordan, John & Moulin, Jean (2015). French Destroyers: Torpilleurs d’Escadre & Contre-Torpilleurs 1922–1956. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing.
Rohwer, Jürgen (2005). Chronology of the War at Sea 1939–1945: The Naval History of World War Two (Third Revised ed.). NIP
Whitley, M. J. (1988). Destroyers of World War Two: An International Encyclopedia. NIP
Links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gu%C3%A9pard-class_destroyer


 Latest Facebook Entry -
Latest Facebook Entry -  X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive
X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive Instagram (@navalencyc)
Instagram (@navalencyc)





 French Navy
French Navy Royal Navy
Royal Navy Russian Navy
Russian Navy Armada Espanola
Armada Espanola Austrian Navy
Austrian Navy K.u.K. Kriegsmarine
K.u.K. Kriegsmarine Dansk Marine
Dansk Marine Nautiko Hellenon
Nautiko Hellenon Koninklije Marine 1870
Koninklije Marine 1870 Marinha do Brasil
Marinha do Brasil Osmanlı Donanması
Osmanlı Donanması Marina Do Peru
Marina Do Peru Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Regia Marina 1870
Regia Marina 1870 Nihhon Kaigun 1870
Nihhon Kaigun 1870 Preußische Marine 1870
Preußische Marine 1870 Russkiy Flot 1870
Russkiy Flot 1870 Svenska marinen
Svenska marinen Søværnet
Søværnet Union Navy
Union Navy Confederate Navy
Confederate Navy Armada de Argentina
Armada de Argentina Imperial Chinese Navy
Imperial Chinese Navy Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Mexico
Mexico Kaiserliche Marine
Kaiserliche Marine 1898 US Navy
1898 US Navy Sovietskiy Flot
Sovietskiy Flot Royal Canadian Navy
Royal Canadian Navy Royal Australian Navy
Royal Australian Navy RNZN Fleet
RNZN Fleet Chinese Navy 1937
Chinese Navy 1937 Kriegsmarine
Kriegsmarine Chilean Navy
Chilean Navy Danish Navy
Danish Navy Finnish Navy
Finnish Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Polish Navy
Polish Navy Romanian Navy
Romanian Navy Turkish Navy
Turkish Navy Royal Yugoslav Navy
Royal Yugoslav Navy Royal Thai Navy
Royal Thai Navy Minor Navies
Minor Navies Albania
Albania Austria
Austria Belgium
Belgium Columbia
Columbia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cuba
Cuba Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Haiti
Haiti Hungary
Hungary Honduras
Honduras Estonia
Estonia Iceland
Iceland Eire
Eire Equador
Equador Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Latvia
Latvia Liberia
Liberia Lithuania
Lithuania Mandchukuo
Mandchukuo Morocco
Morocco Nicaragua
Nicaragua Persia
Persia San Salvador
San Salvador Sarawak
Sarawak Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela Zanzibar
Zanzibar Warsaw Pact Navies
Warsaw Pact Navies Bulgaria
Bulgaria Hungary
Hungary

 Bundesmarine
Bundesmarine Dutch Navy
Dutch Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Marina Militare
Marina Militare Yugoslav Navy
Yugoslav Navy Chinese Navy
Chinese Navy Indian Navy
Indian Navy Indonesian Navy
Indonesian Navy JMSDF
JMSDF North Korean Navy
North Korean Navy Pakistani Navy
Pakistani Navy Philippines Navy
Philippines Navy ROKN
ROKN Rep. of Singapore Navy
Rep. of Singapore Navy Taiwanese Navy
Taiwanese Navy IDF Navy
IDF Navy Saudi Navy
Saudi Navy Royal New Zealand Navy
Royal New Zealand Navy Egyptian Navy
Egyptian Navy South African Navy
South African Navy






























 Ukrainian Navy
Ukrainian Navy dbodesign
dbodesign